Module 9 Test v1
Multiple Choice
-
Meiosis II differs from Mitosis in that
- homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis II, but sister chromatids separate in mitosis.
- meiosis II produces haploid daughter cells, while mitosis produces diploid daughter cells.
- sister chromatids line up during metaphase II, but homologous chromosomes line up in metaphase in mitosis
- DNA replication occurs prior to meiosis II but not prior to mitosis.
- meiosis II produces 2n cells, while mitosis produces n cells.
-
A pair of homologous chromosomes consists of
- 4 non-identical chromatids, each with its own centromere
- 1 pair of sister chromosomes
- 2 non-identical chromatids
- 1 duplicated chromosome
- 1 pair of sister chromatids
-
Koalas have a total of 8 pairs of chromosomes. At the end of meiosis, koalas would produce gametes with a total of
- 2 chromosomes
- 4 chromosomes
- 8 chromosomes
- 16 chromosomes
- 32 chromosomes
-
Which of the following is the correct arrangement of genetic material from largest to smallest in size?
- Chromatin, nucleotides, double helix DNA, sister chromatids, non-duplicated chromosome.
- Sister chromatids, non-duplicated chromosome, chromatin, double helix DNA, nucleotides.
- Nucleotides, double helix DNA, chromatin, non-duplicated chromosome, sister chromatids.
- Double helix DNA, nucleotides, chromatin, sister chromatids, non-duplicated chromosome.
- Nucleotides, chromatin, double helix DNA, sister chromatids, non-duplicated chromosome.
-
Which of the following statements is true regarding the number of chromosomes in humans?
- Humans have 22 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes.
- Humans have 23 pairs of autosomes.
- The number of chromosomes is generally unique to everyone.
- Humans have 22 pairs of autosomes and 2 pairs of sex chromosomes.
- Humans have 44 autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes.
-
If an organism has the chromosome number 2n = 5 (in other words, 5 pairs of chromosomes), how many ways can the chromosomes line up during metaphase I?
- 5
- 10
- 16
- 25
- 32
-
During cellular reproduction, if a cell does not meet the requirements at a checkpoint of the cell cycle, what would happen to the cell given that all the checkpoints are functional?
- Nondisjunction
- Apoptosis
- Cytokinesis
- Independent assortment
- Crossing over
-
Which of the following are risk factors are known to cause cancer? Select all the apply.
- Exposure to UV radiation (sunlight)
- Exposure to cigarette smoke
- Exposure to X-rays
- Exposure to plants and herbs
- Genetics/Family history
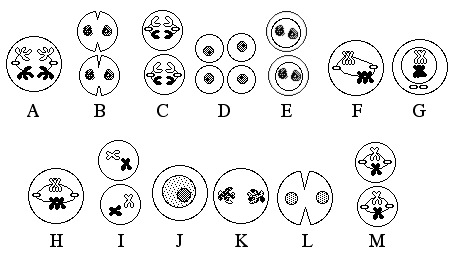
For Questions 9-12, refer to the image and answer choices below.
- Prophase I
- Metaphase I
- Anaphase I
- Telophase I
- Cytokinesis
- Prophase II
- Metaphase II
- Anaphase II
- Telophase II
-
Identify the meiosis phase labeled C. Anaphase II
- Identify the meiosis phase labeled K. Telophase I
- Identify the meiosis phase labeled M. Metaphase II
-
Identify the meiosis phase labeled I. Prophase II
For Questions 13-15, use the following answer choices:
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
- Cytokinesis
- Checkpoint
- G1 phase
- G2 phase
- S phase
-
During which phase does nuclear membrane begin to form? Telophase
- During which phase are chromosomes duplicated? S phase
- During which phase does the cytoplasm of the cell completely separate? Cytokinesis
-
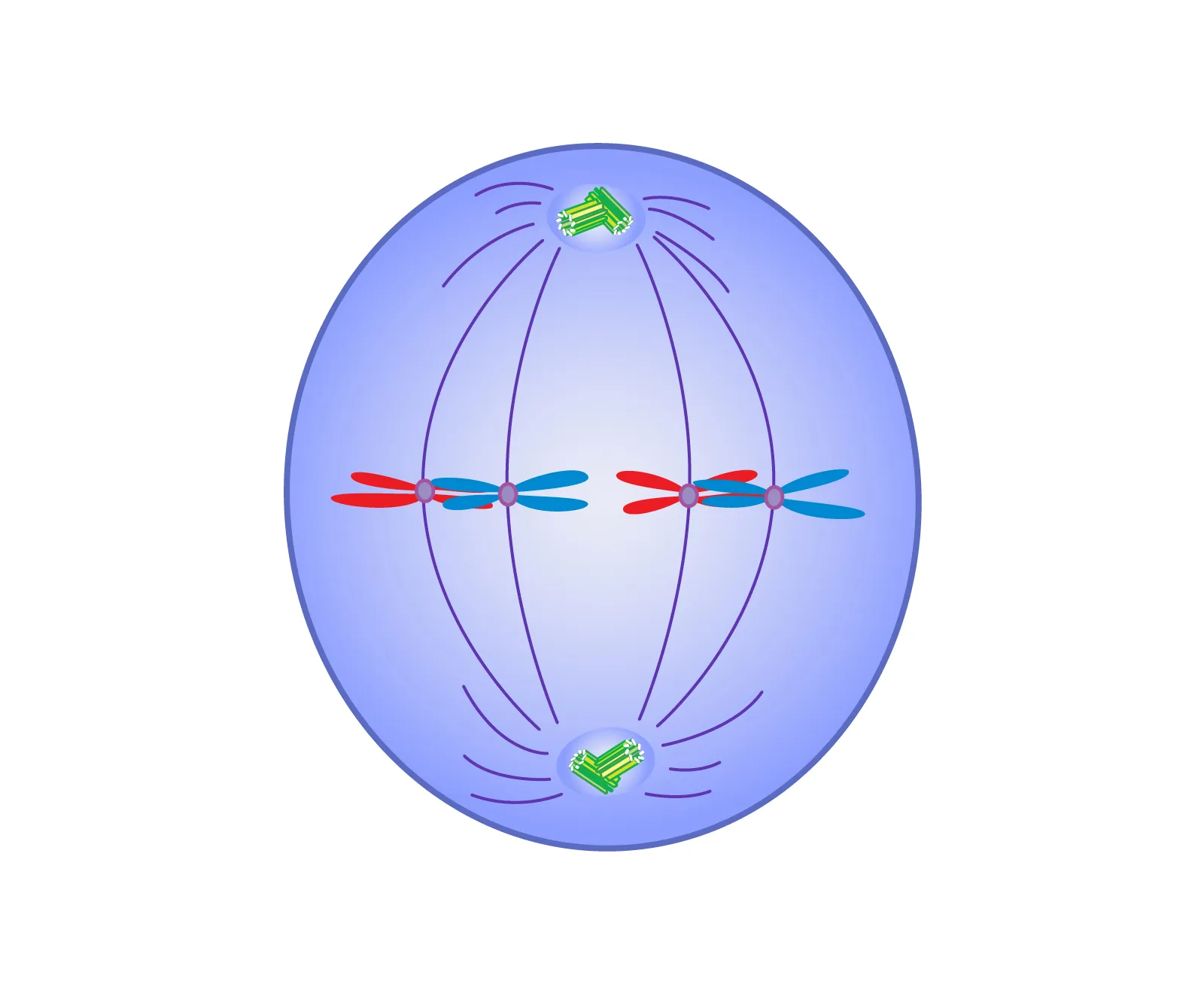
Select the phase the diagram below depict.
Metaphase
-
In order to ensure efficient diffusion of materials into and out of the cell, cells must have:
- high surface area to volume ratio
- low surface area to volume ratio
- high numbers of centrioles
- low numbers of microtubules
- high IQ
-
How does crossing over in prophase I contribute to genetic diversity?
- Some genes are exchanged between sister chromatids of a duplicated chromosome.
- Some genes are exchanged between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
- Some genes move from one pair of chromosomes to another pair of chromosome.
- More genes are added to the chromosomes and exchanged between sister chromatids.
- All the genes in homologous chromosomes are swapped.
-
Aneuploidy screening identifies couples at risk of having a baby with a genetic syndrome while carrier screening shows the likelihood of the baby having an abnormal number of chromosomes.
- True
- False
-
Fertilization creates genetic diversity by allowing each parent to randomly contribute a unique set of genes to a newly fertilized cell.
- True
- False
-
Most of our body cells spend the most amount of time in interphase of the cell cycle.
- True
- False
-
A nucleosome is DNA wrapped around histone proteins.
- True
- False
-
Chromatin fibers condense/supercoil to become chromosomes during G1 phase of the cell cycle.
- True
- False
-
Individuals with Down syndrome can live to adulthood and make significant contributions to their companies and communities.
- True
- False
-
BONUS: If two individuals who have Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21) decide to have children, what is most certain to happen?
- As individuals with 47 chromosomes each, they will have children with 48 chromosomes.
- Most of their children will have Down Syndrome, as it is a disease.
- They have low reproduction rates due to chromosomes unable to pair correctly in Metaphase I.
- Down Syndrome individuals will die before they can reproduce.
- They will not be able to produce normal diploid (2n) children.
Short Answer
Part A
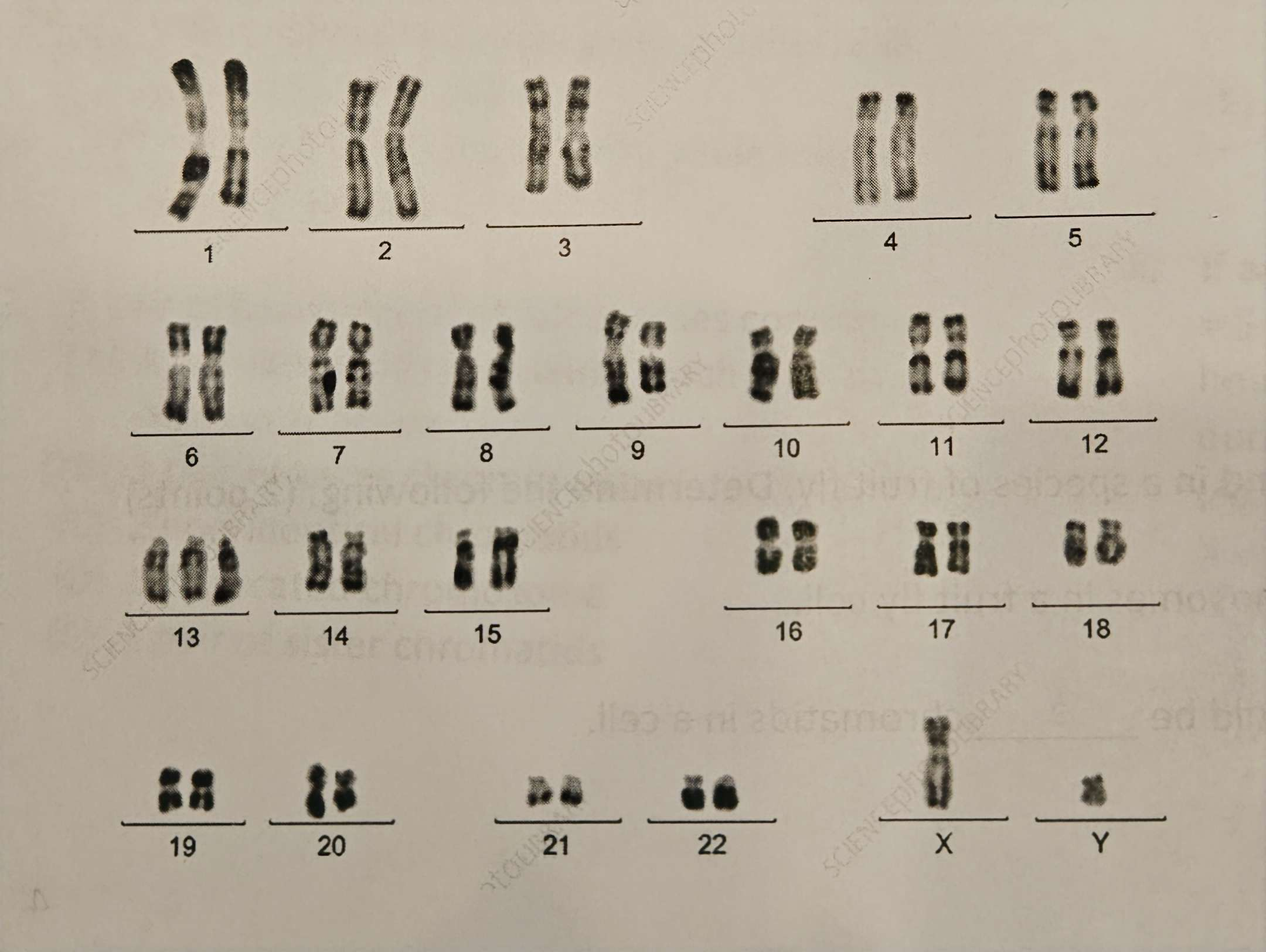
The karyotype of a fetus is shown below:
- Identify the genetic diagnosis AND the gender of the fetus. (1 point)
- Looking at the specific chromosome causing the genetic diagnosis above, the medical professional identified th all 3 of the chromatids are not identical. Determine which type of nondisjunction occurred and explain your answer. (2 points)
Part B
- Identify ONE similarity of ONE difference between Anaphase of mitosis and Anaphase I of meiosis. Ensure the use of proper vocabulary. (1 point)
- Name the process in Meiosis that results in gametes that are uniquely different due to each pair of chromosome aligning randomly before separating. Briefly describe the process identified. (2 points)
- The picture above shows the chromosomes found in a species of fruit fly. Determine the following: (2 points)
- In Prophase, there would be 3 chromosomes in a fruit fly cell.
- In the beginning of Anaphase II, there would be 3 chromatids in a cell.