Unit 1 Review
- Earth's Sphere
- Earth System: All the matter, energy, and processes within Earth's boundary
- Consists of non-living & living things.
- Example: Living things - Trees, animals, and people
- Example: Non-living things - Rocks, air, and water
- 5 main parts
- Geosphere: Mostly solid, rocky part of Earth
- Extends from the center of Earth
- 3 different layers
- Crust
- 5 - 10 km thick (oceanic)
- 35 - 70 km thick (continental)
- Least dense
- Mantle
- 2,900 km thick
- More dense than crust
- Core
- 3,500 km thick
- Most dense
- Crust
- Hydrosphere: The part of Earth that is liquid water
- Includes marshes, ponds, lakes, water droplets, and rain
- Cryosphere: The part made up of all the frozen water on Earth.
- Includes ice, sea ice, glaciers, ice shelves, and icebergs
- Atmosphere: Mostly made up of invisible gases that surround Earth.
- 500 - 600 km of the Earth's surface
- Parts
- 78% nitrogen
- 21% oxygen
- 1% other gases, including argon, carbon dioxide, and water vapor
- Biosphere: The part of Earth made up of living things and the areas of Earth where they are found
- Rocks, soil, ocean, lakes, rivers, and lower atmosphere support life.
- Most organisms need water, and oxygen or carbon dioxide to live
- Geosphere: Mostly solid, rocky part of Earth
- How the spheres interact
- Exchanging Matter: Earth's spheres interact as matter moves between spheres
- Example: Atmosphere →Hydrosphere or Cryosphere → clouds
- Exchanging Energy: Earth's spheres also interact as energy moves between them.
- Example: Plants use solar → generates food
- Exchanging Matter: Earth's spheres interact as matter moves between spheres
- Source of Earth's energy
- Almost all the Earth's energy comes from the sun.
- Energy budget: A way to keep track of energy transfers into and out of the Earth system.
- Unbalancing the budget
- Can cause increase or decrease global temperatures, increase greenhouse gases, which makes us lose polar ice caps.
- Statistics
- Energy coming in
- 26% Reflected by clouds & atmosphere
- 4% Reflected by surface
- 19% Absorbed by clouds and atmosphere
- 51% absorbed by Earth
- Outgoing Energy
- 64% radiated from atmosphere and clouds (19% came from absorption)
- 7% lost as heat rising through the air
- 23% evaporated from Earth to clouds
- 6% radiated from Earth to space
- Energy coming in
- Unbalancing the budget
- Consists of non-living & living things.
- Earth System: All the matter, energy, and processes within Earth's boundary
- Weathering
- Physical Weathering
- Temperature Change [Ice Wedging]
- Water collects in cracks in rock
- Water freezes
- When frozen, it expanded, causing a crack
- Repeats over and over, until splitting the rock
- Pressure Change [Exfoliation]
- Pressure increases outer layers of the rock peel away
- Wind, Water, And Gravity [Abrasion]
- Wind
- Can blast particles away from object
- Water
- Rocks are tumbled and worn out in the running water
- Gravity
- Rocks can crack during landslides
- Wind
- Plant Growth
- Root digs into a small crack in the wall
- Roots expands as the plant grows
- Bigger crack forms
- Temperature Change [Ice Wedging]
- Chemical Weathering
- Oxygen Reactions [Oxidation]
- Different atoms combine with oxygen, making new materials
- Acid
- Precipitation
- Acid falls from the sky, burning rocks or objects in its path
- Groundwater
- Can burn minerals away from and object, depositing them somewhere else
- Living Things
- Plants can create acids, burning away the rock
- Precipitation
- Oxygen Reactions [Oxidation]
- Physical Weathering
- Erosion: The process by which sediment and other materials are moved from one place to another
- Forms of Erosion
- Canyons & Valleys: When a flow of water through streams and rivers erode rock from the streambed
- Caves: Water erodes the rock, eventually forming a cave
- Sea Cliffs: When waves erode and undercut rock to make steep slopes
- Wave cut platforms: When sea cliffs erode so much that the they are flat
- Sea Caves: When the bottom of sea cliffs erode faster than the top
- Sea Arches: When a sea cave erodes all the way to the other side, forming a hole
- Sea stacks: When a sea arch collapses, it leaves behind pillars of rock
- Forms of Erosion
- Deposition: The process by which eroded material is dropped
- Forms of Deposition
- Floodplains: When sediment is dropped over a flooded land
- Deltas: Streams deposit sediment in a fan-shaped pattern
- Alluvial Fan: A dry fan-shaped pattern of sediment
- Beaches: Particles can come up on a beach
- Forms of Deposition
-
Erosion and Deposition with Wind
- Abraded Rock: When wind blows sand against a surface, it can wear it down
- Results of this can lead to smooth, polished surfaces
-
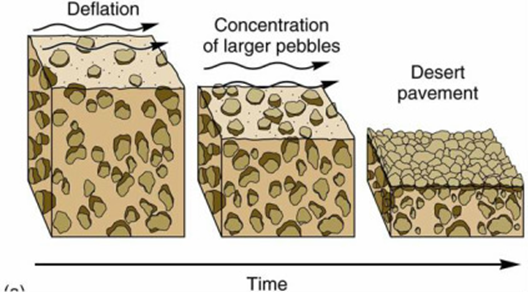
Desert Pavement
- Deflation: The removal of sediment by wind.
- Wind removes sediments, but major rocks stay
-
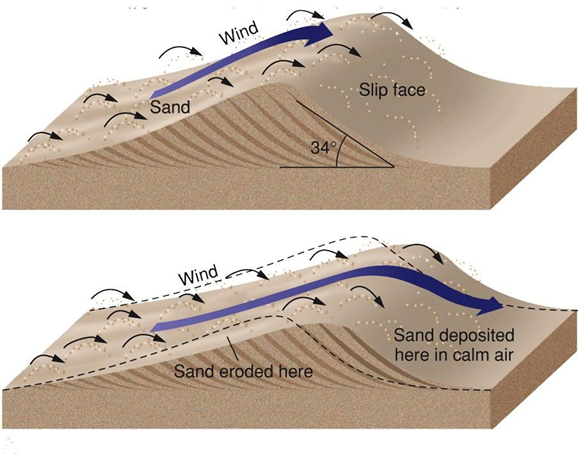
Dunes
- Wind blows sediment on a small mound, dropping sediment on the mound
- Eventually, sediment builds up on the mound
-
Loess: Fine grained sediments that can be carried long distances by wind
- Erosion and Deposition with Ice
- Flowing Ice
- Glacial Drift: When a glacier leaves behind sediments it had carried
- Alpine Glaciers: A glacier that forms in a mountainous area
- Landforms
- Can form U-shaped valleys
- Rivers form V-shaped valleys
- Cirques: A bowl shaped depressions where glacial ice cuts back into the mountain walls
- Arêtes: Jagged ridges that form between two or more cirques that cut into the same mountain
- Horns: Sharp, pyramid-shaped peaks that form when several arêtes join at the top of a mountain
- Hanging valleys: Small glacial valleys that join the deeper, main valley. [It may contain small waterfalls]
- Landforms
- Continental Glaciers: Thick sheets of ice that may spread over large areas, including across entire continents
- Can erode and remove features that existed before the ice appeared
- Erosion and Deposition with Gravity
- Slow Mass Movement
- Creep: The extremely slow movement of material downslope
- Rapid Mass Movement
- Rockfall: When loose rocks fall down a steep slope
- Landslide: A sudden and rapid movement of a large amount of material downslope
- Mudflow: When a large amount of water mixes with soil and rock [This can cause slippery mud to flow down a mountain side]
- Abraded Rock: When wind blows sand against a surface, it can wear it down
Gas Giants and The Solar Eclipse
Gas Giants
- Gas Giants have deep,massive gas atmospheres,which are made up mostly of hydrogen and helium
- Saturn is the least dense planet made up of mostly made up of hydrogen and helium.It could float on water.
- Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system.It’s volume can contain more than 900 Earths.It’s mass is twice the other planets combined.
- Uranus and Neptune will not be included in the test
- Gas giants gas become denser as you move in
- Saturn is the second largest planet after Jupiter and has giant rings that are huge!
Solar Eclipses
- You can only see the solar eclipse during the day time
- Solar Eclipses happen when the moon blocks the Sun from view the daytime.
- The Solar Eclipse generally happens about two weeks after a lunar eclipse
- The Solar eclipse happens when the sun,moon,and earth are aligned
- A solar eclipse happens at a new moon
Earth's Spheres and Weathering
Lesson 1: Earth’s Spheres
- Earth’s system: is all the matter energy,process,within earth’s boundary
- Geosphere:All the rock and minerals in the Earth.
- Hydrosphere: The portion of Earth that is water.
- Cryosphere: All the ice and frozen water is the Earth.
- Atmosphere: A mixture of gases that surrounds a planet, moon, or other celestial body.
- Biosphere:All the living things in the Earth.
- Energy budget: The net flow of energy into and out of a system.
Lesson 2: Weathering
- Weathering: is the break of rock minerals by physical and chemical
- Physical weathering: The mechanical breakdown of rocks into smaller pieces that is caused by natural processes and that does not change the chemical composition of the rock material
- Ice wedging: when water gets in small cracks in rocks then freezes and the water expands.
- Exfoliation:Exfoliation is when the snow/pressure is removed from the rocks, allowing the rocks to bounce back up.
- Abrasion: The process by which rock is reduced in size by the scraping action of of other rocks driven by water, wind, and gravity
- Chemical weathering:The breakdown of rocks from chemical reactions.
- Oxidation: A chemical reaction in which material combines with oxygen to form new material; in geology, oxidation is a form of chemical weathering
- Acid precipitation and give one example: Rain, sleet, or snow that contains a high contains a high concentration of acids
- Stalactites: Are rocks hanging from the top of the cave that is created by chemical and water
- Stalagmites: Are racks that are created from the dripping water