1.4: Erosion and Deposition with Wind
- Abraded Rock: When wind blows sand against a surface, it can wear it down
- Results of this can lead to smooth, polished surfaces
-
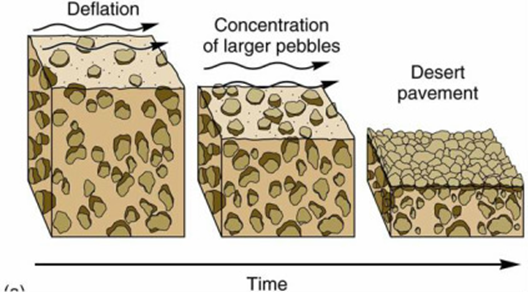
Desert Pavement
-
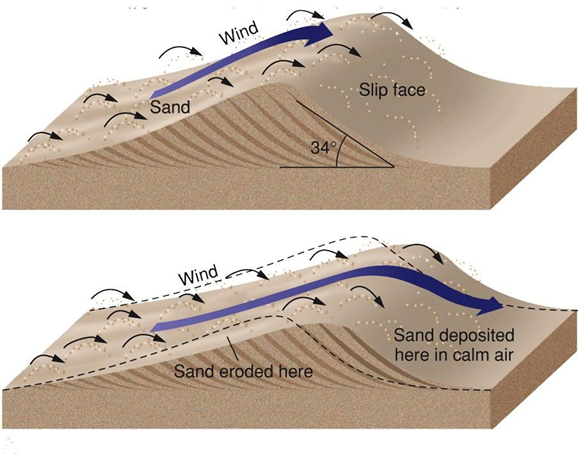
Dunes
-
Loess: Fine grained sediments that can be carried long distances by wind
- Erosion and Deposition with Ice
- Flowing Ice
- Glacial Drift: When a glacier leaves behind sediments it had carried
- Alpine Glaciers: A glacier that forms in a mountainous area
- Landforms
- Can form U-shaped valleys
- Rivers form V-shaped valleys
- Cirques: A bowl shaped depressions where glacial ice cuts back into the mountain walls
- Arêtes: Jagged ridges that form between two or more cirques that cut into the same mountain
- Horns: Sharp, pyramid-shaped peaks that form when several arêtes join at the top of a mountain
- Hanging valleys: Small glacial valleys that join the deeper, main valley. [It may contain small waterfalls]
- Landforms
- Continental Glaciers: Thick sheets of ice that may spread over large areas, including across entire continents
- Can erode and remove features that existed before the ice appeared
- Erosion and Deposition with Gravity
- Slow Mass Movement
- Creep: The extremely slow movement of material downslope
- Rapid Mass Movement
- Rockfall: When loose rocks fall down a steep slope
- Landslide: A sudden and rapid movement of a large amount of material downslope
- Mudflow: When a large amount of water mixes with soil and rock [This can cause slippery mud to flow down a mountain side]